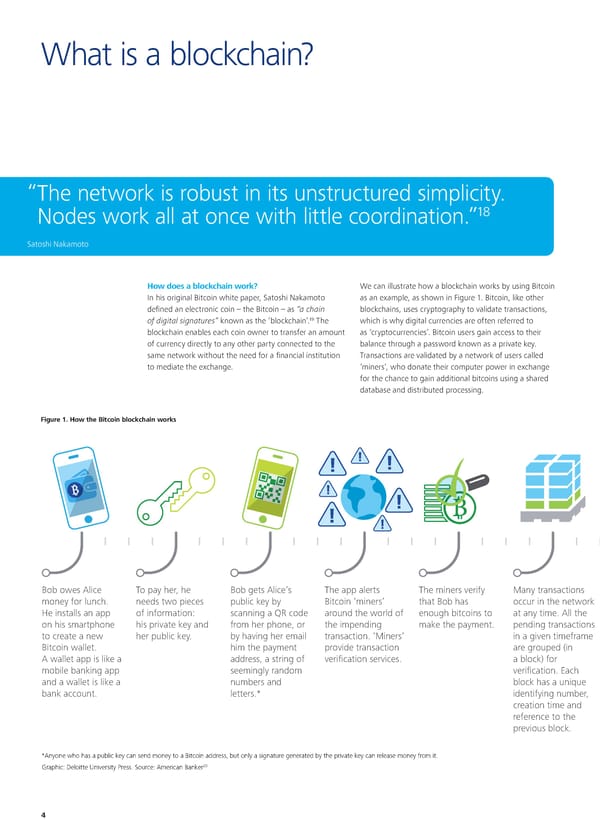
To start a new section, hold down the apple+shift keys and click to release this object and type the section title in the box below. What is a blockchain? “ The network is robust in its unstructured simplicity. 18 Nodes work all at once with little coordination.” Satoshi Nakamoto How does a blockchain work? We can illustrate how a blockchain works by using Bitcoin In his original Bitcoin white paper, Satoshi Nakamoto as an example, as shown in Figure 1. Bitcoin, like other defined an electronic coin – the Bitcoin – as “a chain blockchains, uses cryptography to validate transactions, 19 of digital signatures” known as the ‘blockchain’. The which is why digital currencies are often referred to blockchain enables each coin owner to transfer an amount as ‘cryptocurrencies’. Bitcoin users gain access to their of currency directly to any other party connected to the balance through a password known as a private key. same network without the need for a financial institution Transactions are validated by a network of users called to mediate the exchange. ‘miners’, who donate their computer power in exchange for the chance to gain additional bitcoins using a shared database and distributed processing. Figure 1. How the Bitcoin blockchain works Bob owes Alice To pay her, he Bob gets Alice’s The app alerts The miners verify any transactions The new block is put …hen a miner solves The algorithm …ithin ten minutes All the transactions money for lunch. needs two pieces public key by Bitcoin ‘miners’ that Bob has occur in the network in the network so the cryptographic rewards the of Bob initiating in the block are now He installs an app of information: scanning a code around the world of enough bitcoins to at any time. All the that miners can problem, the winning miner with the transaction, fulfilled and Alice on his smartphone his private key and from her phone, or the impending make the payment. pending transactions verify if its discovery is †‡ bitcoins, and the he and Alice each gets paid. to create a new her public key. by having her email transaction. ‘iners’ in a given timeframe transactions are announced to the new block is added receive the first Bitcoin wallet. him the payment provide transaction are grouped in legitimate. rest of the network. to the front of confirmation that A wallet app is like a address, a string of verification services. a block for ƒerification is the blockchain. the bitcoin was mobile banking app seemingly random verification. €ach accomplished by €ach block ˆoins signed over to her. and a wallet is like a numbers and block has a uni‚ue completing comple„ the prior block so bank account. letters. identifying number, cryptographic a chain is made – creation time and computations. the blockchain. reference to the previous block. Anyone who has a public key can send money to a Bitcoin address, but only a signature generated by the private key can release money from it. †’ Šraphic: ‹eloitte Œniversity Žress. ‘ource: American Banker 4
 Blockchains: Enigma. Paradox. Opportunity. Page 5 Page 7
Blockchains: Enigma. Paradox. Opportunity. Page 5 Page 7